Quantum Monte Carlo Simulations
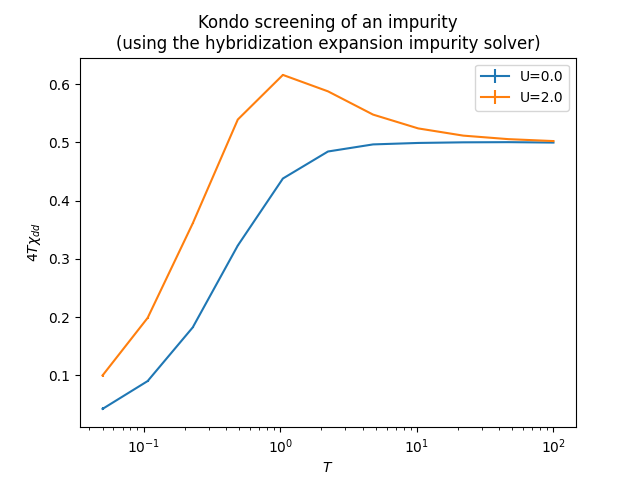
As an example of Quantum Monte Carlo simulation we present a simulation of the effective local moment of the impurity with decreasing temperature due to Kondo screening, with the semielliptical density of states used as a hybridization function.
First, we import all required python modules:
from pyalps.hdf5 import archive # hdf5 interface
import pyalps.cthyb as cthyb # the solver module
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # for plotting results
from numpy import exp,log,sqrt,pi # some mathNow we generate a sequence of $10$ temperatures between $0.05$ and $100.0$ which are equidistant on a logarithmic scale
N_T = 10 # number of temperatures
Tmin = 0.05 # maximum temperature
Tmax = 100.0 # minimum temperature
Tdiv = exp(log(Tmax/Tmin)/N_T)
T=Tmax
Tvalues=[]
for i in range(N_T+1):
Tvalues.append(T)
T/=TdivWe set up the values of the onsite interaction, the number of time points, and the time limit for each simulation:
Uvalues=[0.,2.] # the values of the on-site interaction
N_TAU = 1000 # number of tau-points; must be large enough for the lowest temperature (set to at least 5*BETA*U)
runtime = 5 # solver runtime (in seconds)Then we set up the parameters for the simulation:
values=[[] for u in Uvalues]
errors=[[] for u in Uvalues]
parameters=[]
for un,u in enumerate(Uvalues):
for t in Tvalues:
# prepare the input parameters; they can be used inside the script and are passed to the solver
parameters.append(
{
# solver parameters
'SWEEPS' : 1000000000, # sweeps to be done
'THERMALIZATION' : 1000, # thermalization sweeps to be done
'SEED' : 42, # random number seed
'N_MEAS' : 10, # number of sweeps after which a measurement is done
'N_ORBITALS' : 2, # number of 'orbitals', i.e. number of spin-orbital degrees of freedom or segments
'BASENAME' : "hyb.param_U%.1f_BETA%.3f"%(u,1/t), # base name of the h5 output file
'MAX_TIME' : runtime, # runtime of the solver per iteration
'VERBOSE' : 1, # whether to output extra information
'TEXT_OUTPUT' : 0, # whether to write results in human readable (text) format
# file names
'DELTA' : "Delta_BETA%.3f.h5"%(1/t), # file name of the hybridization function
'DELTA_IN_HDF5' : 1, # whether to read the hybridization from an h5 archive
# physical parameters
'U' : u, # Hubbard repulsion
'MU' : u/2., # chemical potential
'BETA' : 1/t, # inverse temperature
# measurements
'MEASURE_nnw' : 1, # measure the density-density correlation function (local susceptibility) on Matsubara frequencies
'MEASURE_time' : 0, # turn of imaginary-time measurement
# measurement parameters
'N_HISTOGRAM_ORDERS' : 50, # maximum order for the perturbation order histogram
'N_TAU' : N_TAU, # number of imaginary time points (tau_0=0, tau_N_TAU=BETA)
'N_MATSUBARA' : int(N_TAU/(2*pi)), # number of Matsubara frequencies
'N_W' : 1, # number of bosonic Matsubara frequencies for the local susceptibility
# additional parameters (used outside the solver only)
't' : 1, # hopping
'Un' : un, # interaction point
}
)For each set of parameters, we set up the hybridization function
for parms in parameters:
ar=archive(parms['BASENAME']+'.out.h5','a')
ar['/parameters']=parms
del ar
print("creating initial hybridization...").
g=[]
I=complex(0.,1.)
mu=0.0
for n in range(parms['N_MATSUBARA']):
w=(2*n+1)*pi/parms['BETA']
g.append(2.0/(I*w+mu+I*sqrt(4*parms['t']**2-(I*w+mu)**2))) # use GF with semielliptical DOS
delta=[]
for i in range(parms['N_TAU']+1):
tau=i*parms['BETA']/parms['N_TAU']
g0tau=0.0;
for n in range(parms['N_MATSUBARA']):
iw=complex(0.0,(2*n+1)*pi/parms['BETA'])
g0tau+=((g[n]-1.0/iw)*exp(-iw*tau)).real # Fourier transform with tail subtracted
g0tau *= 2.0/parms['BETA']
g0tau += -1.0/2.0 # add back contribution of the tail
delta.append(parms['t']**2*g0tau) # delta=t**2 g
# write hybridization function to hdf5 archive (solver input)
ar=archive(parms['DELTA'],'w')
for m in range(parms['N_ORBITALS']):
ar['/Delta_%i'%m]=delta
del arFinally, we run the Monte Carlo simulation for each set of parameters.
for parms in parameters:
# solve the impurity model in parallel
cthyb.solve(parms)After the simulation is finished, we obtain results for each set of parameters, postprocess them, and plot them.
for parms in parameters:
# extract the local spin susceptiblity
ar=archive(parms['BASENAME']+'.out.h5','w')
nn_0_0=ar['simulation/results/nnw_re_0_0/mean/value']
nn_1_1=ar['simulation/results/nnw_re_1_1/mean/value']
nn_1_0=ar['simulation/results/nnw_re_1_0/mean/value']
dnn_0_0=ar['simulation/results/nnw_re_0_0/mean/error']
dnn_1_1=ar['simulation/results/nnw_re_1_1/mean/error']
dnn_1_0=ar['simulation/results/nnw_re_1_0/mean/error']
nn = nn_0_0 + nn_1_1 - 2*nn_1_0
dnn = sqrt(dnn_0_0**2 + dnn_1_1**2 + ((2*dnn_1_0)**2) )
ar['chi']=nn/4.
ar['dchi']=dnn/4.
del ar
T=1/parms['BETA']
values[parms['Un']].append(T*nn[0])
errors[parms['Un']].append(T*dnn[0])
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel(r'$T$')
plt.ylabel(r'$4T\chi_{dd}$')
plt.title('Kondo screening of an impurity\n(using the hybridization expansion impurity solver)')
for un in range(len(Uvalues)):
plt.errorbar(Tvalues, values[un], yerr=errors[un], label="U=%.1f"%Uvalues[un])
plt.xscale('log')
plt.legend()
plt.show()After that, you will have the following plot: